2022 sees rise in ‘unwanted’ emails as phishing attacks remain popular
A large proportion of your work emails may not be useful in any way, a new report examining billions of messages has claimed.
Research from Hornetsecurity analyzing 25 billion business emails found nearly half (40.5%) are ‘unwanted’, and could even represent a serious threat to businesses.
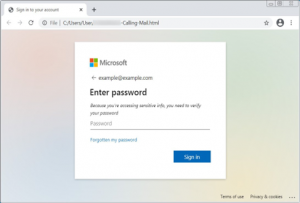
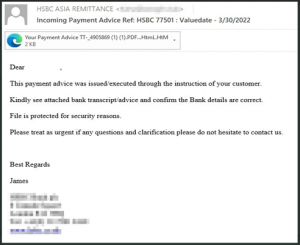
The report also revealed how email remains an incredibly popular threat vector, with the most common kind of malicious messages being phishing attacks – emails pretending to be from well-known companies, sometimes quite convincingly – which made up 39.6% of all threats.
False sense of security
When it comes to malicious email attachments, Archive files such as Zip made up the greatest proportion (28% of messages), followed by web files (HTML) at 21%. Text based files were also commonly employed, with tainted Microsoft Word documents making up 12.7%, PDF 12.4% and Excel 10.4%.
The report also found new methods are being developed by cybercriminals in response to the changing digital landscape. For instance, attacks exploiting the macro capabilities in Microsoft 365 are no longer viable since Microsoft disabled the feature last year, specifically to shore up its security.
As a result of this, new tactics have been adopted. HTML smuggling has risen, where hidden LNK or ZIP files are contained within web links to deploy malware.
Hornetsecurity CEO Daniel Hofmann warned that given the prevalence of cloud based systems, such as Microsoft 365, their use should merit the same level of caution. Hornetsecurity’s report found that a quarter of respondents did not know that 365 could be a potential gateway for ransomware – some even presumed it was invulnerable to such threats.
“Ongoing training should be in place to prevent fraudsters from manipulating the trust people have in Microsoft and other office systems”, Hoffman advised. He also made specific mention of Microsoft Teams, adding that “it’s also critical to ensure all data shared via this platform is backed up.”
Other reports have found a similarly high – or even higher – proportion of spam emails in people’s accounts. Recent findings from Kaspersky, for instance, put the figure between 45-85%.
If you are looking for an expert to help you find the best solutions for your business talk to GCInfotech about a free technology assessment
Published with consideration from TechRadar SOURCE