Phishing attacks have evolved dramatically in recent years, and the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has made them more sophisticated than ever. Gone are the days of poorly written emails with obvious spelling mistakes. Today’s phishing attempts often look legitimate, leveraging AI to mimic corporate branding, write flawless text, and even personalize messages based on publicly available data. This makes identifying phishing emails a critical skill for individuals and organizations alike.
Why AI Makes Phishing More Dangerous
AI-powered tools allow cybercriminals to:
- Generate convincing content: AI can craft professional-looking emails that mimic tone and style of real companies.
- Personalize attacks: By scraping social media and public profiles, attackers can tailor messages to specific individuals.
- Automate scale: AI enables mass phishing campaigns with minimal effort, increasing the likelihood of success.
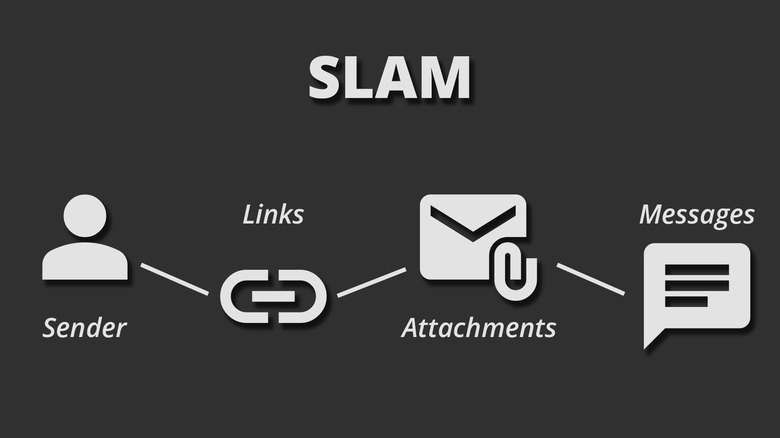
Key Indicators of Phishing Emails
Despite their sophistication, phishing emails often share common traits. Here’s what to look for:
- Suspicious Sender Address
- Check the email domain carefully. Attackers often use addresses that look similar to legitimate ones (e.g., support@micros0ft.com instead of support@microsoft.com).
- Unexpected Requests
- Be wary of emails asking for sensitive information, urgent payments, or login credentials. Legitimate companies rarely request this via email.
- Generic Greetings
- Even with AI personalization, some phishing emails still use vague greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of your name.
- Links and Attachments
- Hover over links before clicking. If the URL looks strange or doesn’t match the sender’s domain, it’s a red flag.
- Avoid opening unexpected attachments, especially if they prompt you to enable macros.
- Sense of Urgency
- Phrases like “Act Now” or “Your account will be suspended” are common tactics to pressure quick action.
- Inconsistent Branding
- AI can replicate logos and colors, but subtle inconsistencies in design or formatting may indicate a fake.
How to Stay Protected
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Even if credentials are stolen, MFA adds an extra layer of security.
- Use Email Security Tools: Advanced filters and AI-based detection systems can help identify suspicious emails.
- Educate Your Team: Regular training on phishing awareness is essential.
- Report and Verify: If in doubt, contact the sender through official channels—not by replying to the suspicious email.
The Bottom Line
AI has made phishing smarter, but vigilance and layered security can keep you safe. By combining human awareness with advanced security tools, organizations can stay ahead of these evolving threats.